IA e Microsoft Azure
-
Denis Dal Molin
- 28 Jan, 2025
- 20 Mins read

Versione italiana a seguire
Introduction
Artificial intelligence has become part of our everyday lives, significantly changing our approach to work, communication, and decision-making. The full potential of AI emerges when it is combined with the scalability and power of cloud computing, allowing complex models to be trained and deployed at large scale with agility and flexibility.
In this domain, Microsoft Azure is positioned as a leader in democratizing access to these technologies, offering a versatile platform integrating AI into business processes.
Fundamental concepts
To understand the potential of artificial intelligence, it is essential to start with its foundations. AI is based on mathematical models and algorithms that are trained. It is a discipline that focuses on developing systems that can simulate human behavior.
Among its main components is Machine Learning (ML), a central method by which the systems learn from data, improving their understanding without the need for explicit programming. In other words, it enables models to identify connections and trends called patterns within large datasets to accomplish tasks.
A key aspect of Machine Learning is model training, a process of feeding the system with labeled (or unlabelled) data to “teach” it to make predictions. For example, a model can be trained to recognize spam or non-spam emails by analyzing thousands of past examples.
The applications of ML can be divided into three main categories: classification, such as distinguishing cat images from dog images, identifying objects, etc. Regression, such as predicting the price of a house based on characteristics such as location and square footage; and clustering, such as grouping users with similar behaviors on a website to personalize their experience.
A significant evolution in the field is Deep Learning, which uses neural networks inspired by the workings of the human brain. This approach underlies advanced technologies such as speech recognition and Large Language Models (LLMs) such as those used in generative AI systems.
Among the most well-known and currently used Large Language Models (LLMs) are:
- GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer) from OpenAI: uses billions of parameters to answer questions.
- LLaMA from Meta: Open-source model designed to be lighter.
- Claude from Anthropic: The philosophy of the model is based on responsible use.
The heart of the success of these models lies in the training and validation process. After training, the model is tested on a separate data set to assess its ability to generate output, a key step in avoiding the problem of overfitting, in which a model responds well only to training data but fails on new data.
Main use cases
The main use cases include:
- Predictions and forecasting: The ability to analyze historical data to predict future events, such as customer behavior or market demand.
- Anomaly detection: detecting deviations from normal usage patterns, essential for security, fraud monitoring, and maintaining complex systems.
- Natural language processing (NLP): The ability to take text, understand it, and respond appropriately, as occurs in translation systems or sentiment analysis.
- Computer vision: the ability to process images and return information, such as in the recognition of objects, faces, or situations in images and videos.
- Conversational AI: Enabling machines to communicate with humans through smooth and natural conversations, such as in chatbots or virtual assistants.
These use cases represent only part of the incredible possibilities.
Machine Learning vs Deep Learning
Machine Learning, Deep Learning, and Natural Language Processing are three fundamental areas of artificial intelligence, but each focuses on different aspects of “understanding” and “interacting” with data.
- Machine Learning (ML) is a branch of AI that focuses on developing algorithms that can learn from data.
- Deep Learning (DL) is a subcategory of machine learning that focuses on the use of deep neural networks, that is, machine learning models with multiple layers (layers). These models are designed to simulate how the human brain works and are particularly powerful when it comes to working with large volumes of unstructured data, such as images, audio, or text. Deep learning underlies technologies such as speech recognition, computer vision (such as facial recognition,) and machine automatic translation.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP) focuses on the interaction between computers and human language. It can advantage of both, machine learning, and deep learning techniques to improve language understanding.
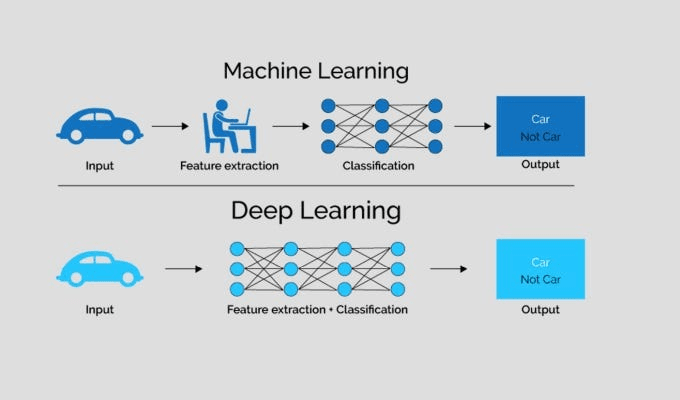
Then there are other important areas such as Computer Vision, which enables computers to “see” and understand the content of images and videos. Others are still under development such as Quantum Computing, which uses the principles of quantum mechanics to process information that is not possible with traditional supercomputers.
Models
To create a machine learning model, the first key element is an algorithm, which is a set of instructions that the model uses to learn from the data. In simplistic terms, we can imagine a model as a mathematical function, represented by the formula y=f(x), where x represents the input (data) and y represents the output (expected result).
A central concept in building a model is the role of features and labels within the training dataset.
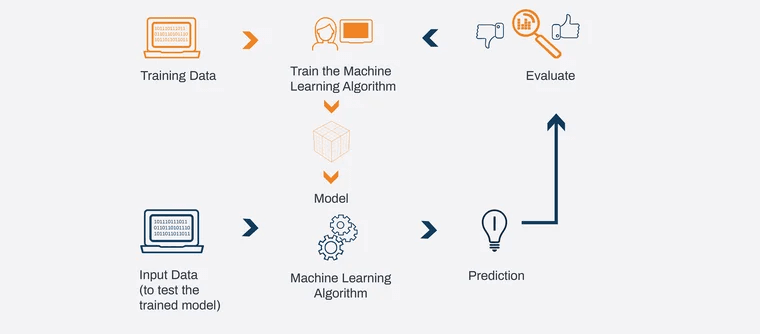
Features are the attributes or independent variables that describe the data, while labels are the outcome or dependent variable we want to predict. For example, in a dataset analyzing user behavior, a feature might be “time spent on the site,” while the label might be “purchase made: yes/no.”
Before the data can be used for learning, it is essential to subject it to a preparation and processing process (ETL: Extract, Transform, Load). During this phase, we inspect the data to ensure that it is clean and ready to use, removing missing values, handling outliers, and transforming the information into a suitable format. In addition, we can apply feature engineering techniques to create new features based on existing ones, thereby improving the performance of the model.
Algorithms, once applied to data, can be distinguished into different learning categories:
- Supervised: The model learns from a labeled dataset, where each input is associated with a known output (e.g., classification or regression).
- Unsupervised: The model works on unlabelled data and tries to find hidden patterns or groups (e.g., clustering);
- Semi-supervised: A combination of the two approaches, in which only part of the data is labeled;
- Reinforcement learning: The model learns through a reward and penalty system, continuously adapting based on feedback (e.g., in games or autonomous driving systems).
What are Transformers?
Transformers are a neural network architecture designed to handle sequential data (such as text, images or audio) by introducing a mechanism called self-attention, which allows the model to analyze the entire sequence simultaneously and assign a weight to each element relative to the others. They are particularly good at capturing relationships between words even if they are far apart in a sentence.
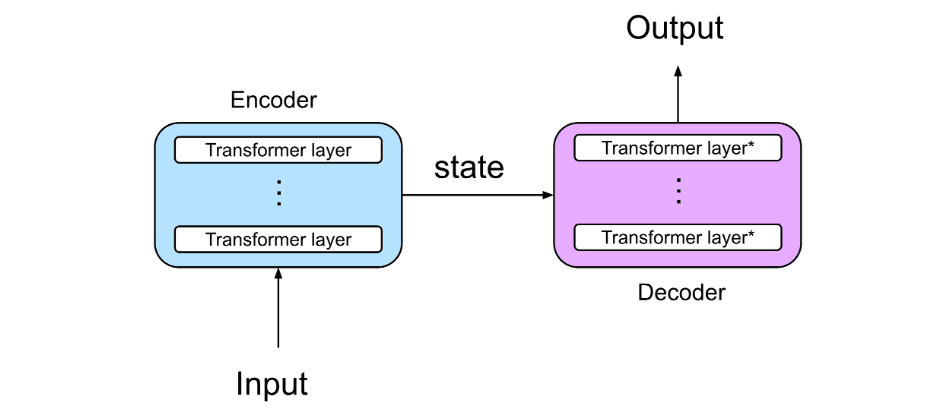
Example: Imagine that you are using a Transformer to complete the sentence, “The sky is very...”
- Input: [“The,” “sky,” “is,” “very.”]
- Self-Attention: Each word looks for relationships with the others (e.g., “very” gives attention to “sky”)
- Output: The model generates a likely word, such as “blue”
This process is repeated word by word until the entire sentence is completed.
What are Tokens?
Tokens are basic units in which a language model, such as "Transformer" which breaks down the text to comprehend (understand) and manipulate it. In a language context, it can represent: words, parts of words, special characters or symbols, phrases, or concepts.
When a language model receives a text as an input, it first breaks it down into tokens. This process is called tokenization. Each token is then associated with a numerical representation, which the model uses to understand the sequence of the text. These numerical vectors are then processed by the model (via the attention mechanism in the case of the Transformer) to generate output, such as answers, translations, or predictions.
Models have a maximum length of tokens they can process, for example, GPT-3 can process up to 4096 tokens in a single input, while GPT-3.5 Turbo 16k goes up to 16000.
The longer the sequence, the more tokens are used, and this can affect the computational cost and quality of responses.
Example: Imagine you have the phrase, “Hello, how are you?”
A simple tokenization process could break it down into:
- “Hello”
- ”,”
- “how”
- “are you”
- “?”
Nat.dev
Nat.dev is a platform designed to facilitate interaction with advanced language models, enabling developers to explore, test, and use modern language models. It offers a playground, i.e., an interactive environment that allows customization of parameters and settings to observe how a model's behavior varies with different variables.
Variables and parameters
When we interact with an advanced language model, there are several variables or parameters that we can change to influence the behavior and results generated in order to achieve more creative, consistent, or tailored responses.
Temperature is one of the main parameters for controlling the creativity and randomness of responses. A lower temperature (e.g., 0.2) makes the model more deterministic and accurate, while a higher temperature (e.g., 1.0 or higher) makes responses more creative, unpredictable, and diverse.
Top-up (also known as “nucleus sampling”) is another creativity control parameter, which establishes the cumulative probability from which the model draws responses. A low top-p (e.g., 0.2) for more predictable responses. A high top-p (e.g., 0.9) for increased variety in responses.
The frequency penalty for the repetition of words or phrases. Increasing this parameter reduces the probability that the model repeats the same words or concepts redundantly. A higher value increases this penalty.
The presence penalty discourages the use of words that have already appeared in the context of the conversation. The higher the value, the less likely the model will repeat topics or words that have already been used.
Stop sequences tell the model when to stop in response generation. You can define one or more text sequences that, if generated by the model, will cause it to stop immediately. This is useful to avoid excessively long or unwanted responses.
Logit bias is a system for altering the probability of certain words or phrases being chosen by the model. It allows the model to be forced to favor (or avoid) specific words in its outputs by altering the logit (the probability measure) of certain choices.
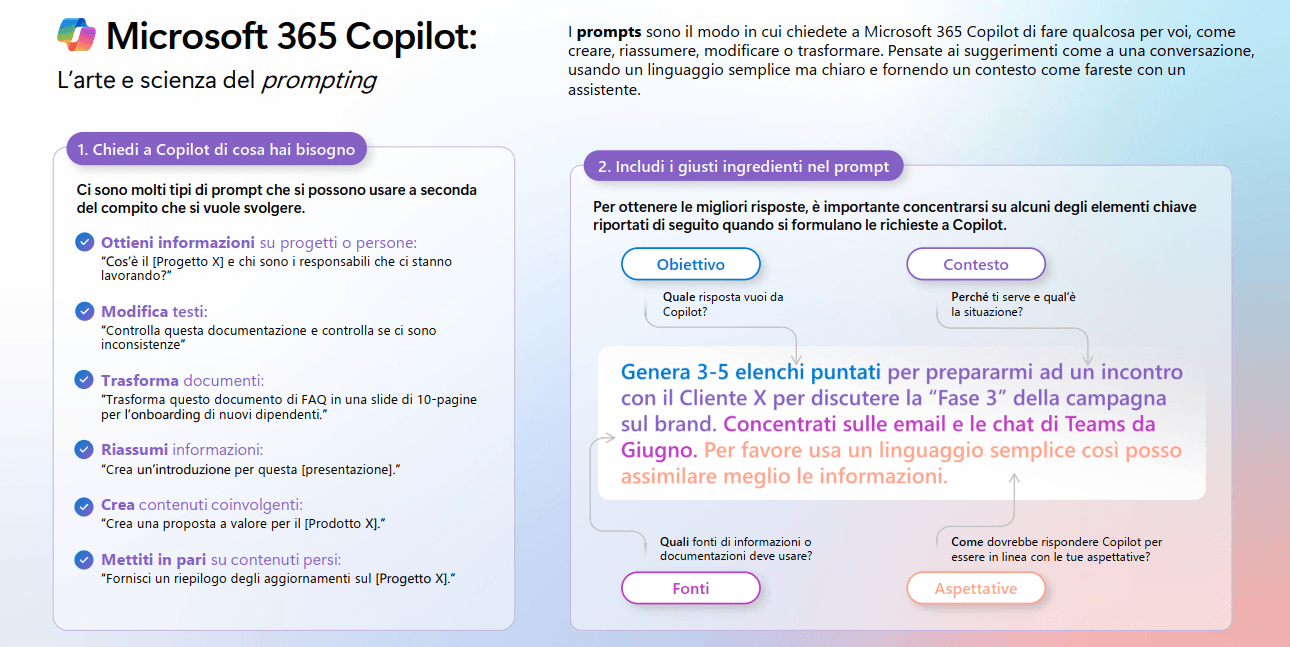
Prompt
The prompt is undoubtedly one of the most crucial elements when interacting with a model. It is the text (the question) we provide as input; its importance cannot be underestimated, as it completely guides the answer we will get (it acts as a directive). If you provide an ambiguous or generic prompt, the answer will probably be just as generic. But if the prompt is precise and clear, the response will be detailed, relevant, and useful. You can use the prompt to influence the tone**** and style of the response. A poorly worded prompt can lead to incorrect or irrelevant results.
An example of how a well-formulated prompt affects the final result is seen in text-to-image models such as Midjourney. Here, the quality of the prompt directly determines the visual output. Unlike language models, where we evaluate consistency and tone, in text-to-image the link between prompt and image is immediate and visible.
Azure Services
Microsoft Azure offers a wide range of cloud services that enable companies to deploy intelligent solutions by leveraging artificial intelligence and machine learning. These services are part of an ecosystem that includes everything from data management to model training to application deployment.
Among these, two main solutions emerge:
- Azure Machine Learning
- Azure Cognitive Services
The differences between the two solutions focus mainly on the approach taken to implementing artificial intelligence, the possibility of customization, and the level of control allowed over the algorithms and models.
Azure Cognitive Services is a set of APIs and AI services pre-built by Microsoft (they cannot be customized for specific use cases except in a limited way). These services allow developers to add artificial intelligence to applications without having to build or train models. It includes natural language recognition, computer vision, speech recognition, and text sentiment analysis. It is useful for projects that require standard features such as chatbots.
Azure Machine Learning is a managed platform for developing, training, and deploying complex machine learning models. It is ideal for data scientists and developers who want to create custom models with advanced algorithms. You can choose the algorithms to use, define the workflow, and train models on specific datasets. It provides complete control over algorithms, workflow, and model training.
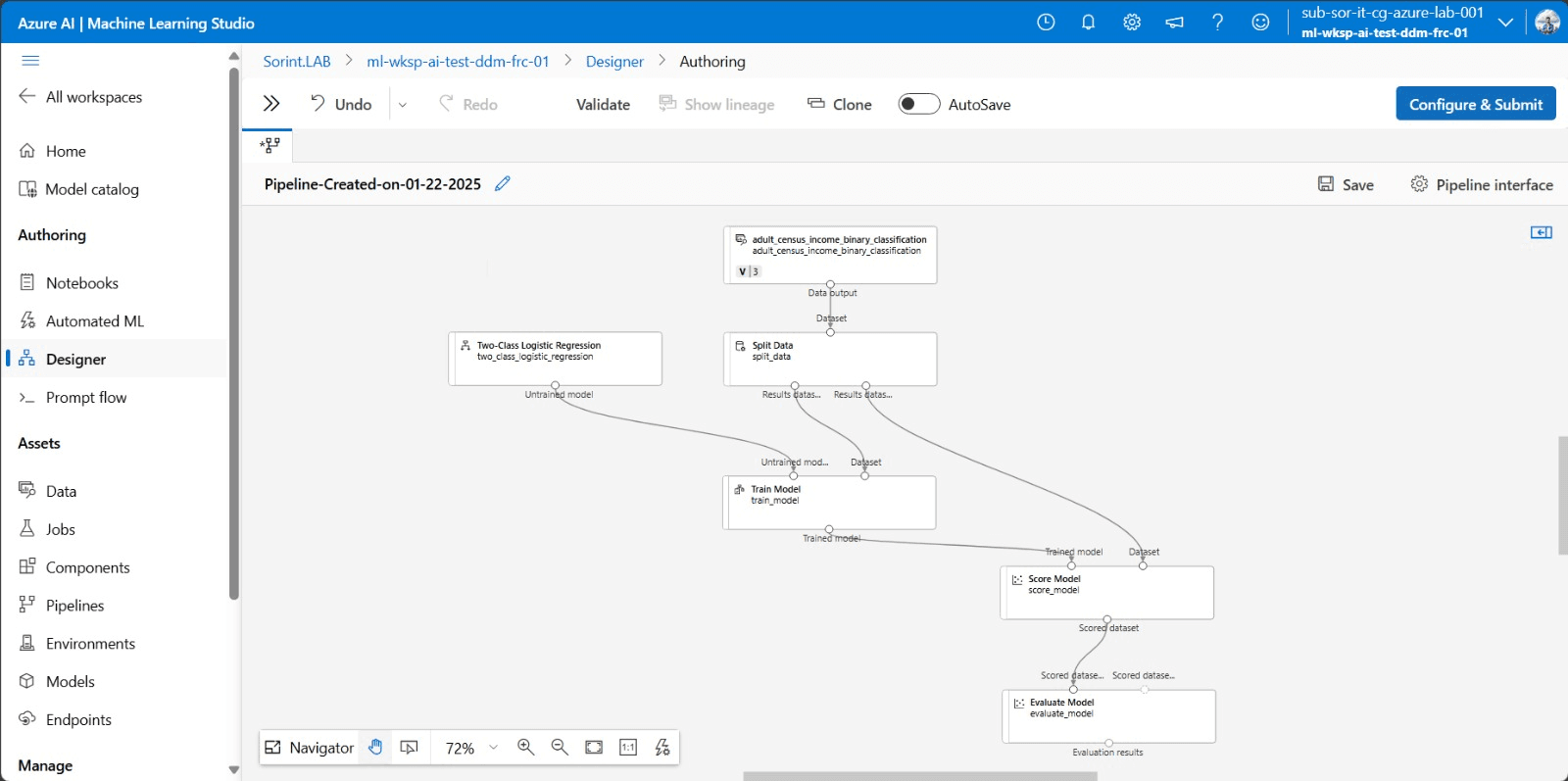
Creation and use of the AML service
The service creation in the Azure portal is a process involving several steps:
- The first step is the creation of a workspace, a workspace that serves as a container for all objects, data, models etc. representing the central point where all activities will be organized.
- The creation of a workspace requires a number of additional resources to efficiently manage data, security, and monitoring of operations: Azure Key Vault, Azure Storage Account, Azure Container Registry, and Application Insights. These resources are configured automatically or manually during environment creation.
Once the workspace is set up, the next step is to open Azure Machine Learning Studio, a graphical platform for visual and interactive creation and management.
The study makes it easy to upload data or use existing samples, which can be divided into sets such as training (70 percent) and test/validation (30 percent).
The Designer is one of the most powerful features in that, with a no-code, drag-and-drop approach, it allows you to build the flow of the model by governing its entire lifecycle.
With the flow built, one can proceed to train the model and once finished do testing and validation. The system also allows real-time monitoring of metrics, such as accuracy and recall for classification models and other performance parameters.
Once the model is ready the next step is deployment, utilizing the various options of Azure Compute:
- Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS): If you want a scalable, highly available environment.
- Azure Container Instances (ACI): A simpler and lighter alternative if your model does not need scalability or complex management.
- Edge Computing: In some cases, you may want to deploy your model directly to edge devices (e.g., IoT)
Service endpoints
When it comes to AI Services in Azure, one of the key aspects concerns interaction with services through endpoints. An endpoint represents a specific URL that allows a service to be invoked through an API call. Requests are sent to such URLs to obtain or send data, such as images, text or input parameters.
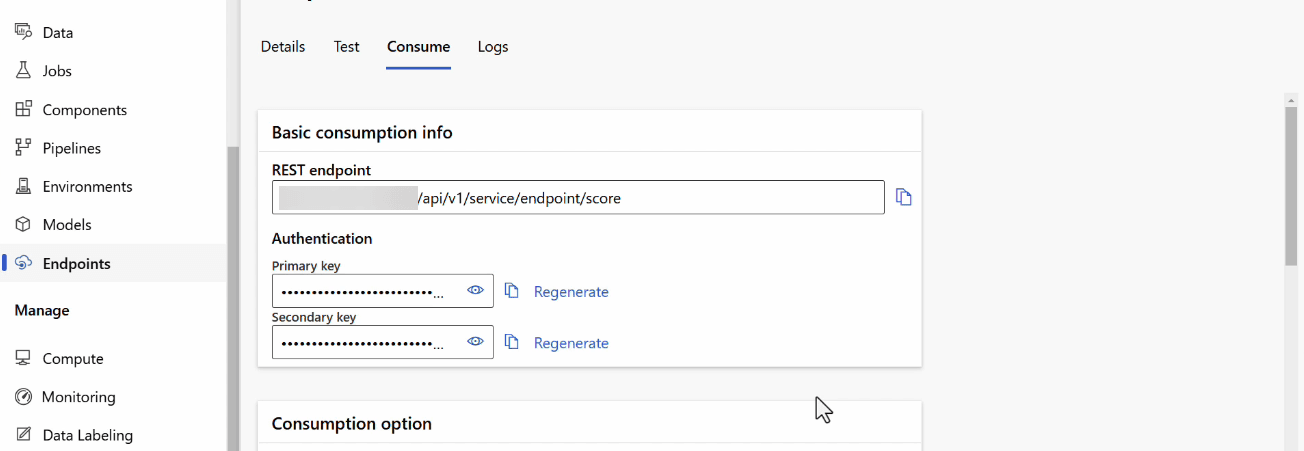
Once retrieved, it can be tested via a REST request. The most commonly used tools for testing and interacting with RESTful APIs are Postman or cURL.
Interacting via Postman
In the specific case of a POST type call, we are passing information to the service to get a processed response. This is the most common way when we are working with data that needs to be processed, such as text or images.
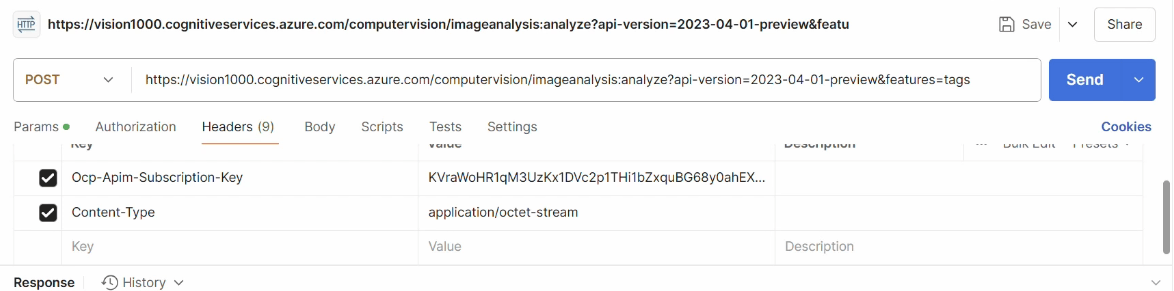
To send such a request, we need to configure two parts correctly**:**
- Header: with the necessary authentication information, we use a bearer token that represents our permission to access the service generated during service creation;
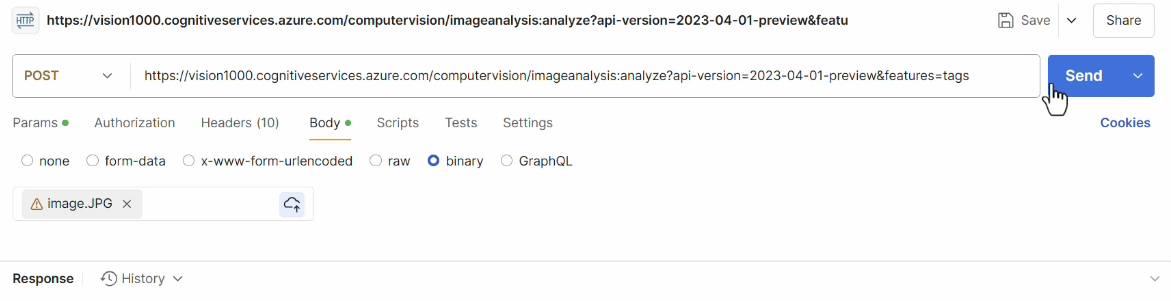
- Body: we have to specify the data we want to send to the service, for this type of service we have to use JSON format, the body should be a string that contains the information needed to process the request.
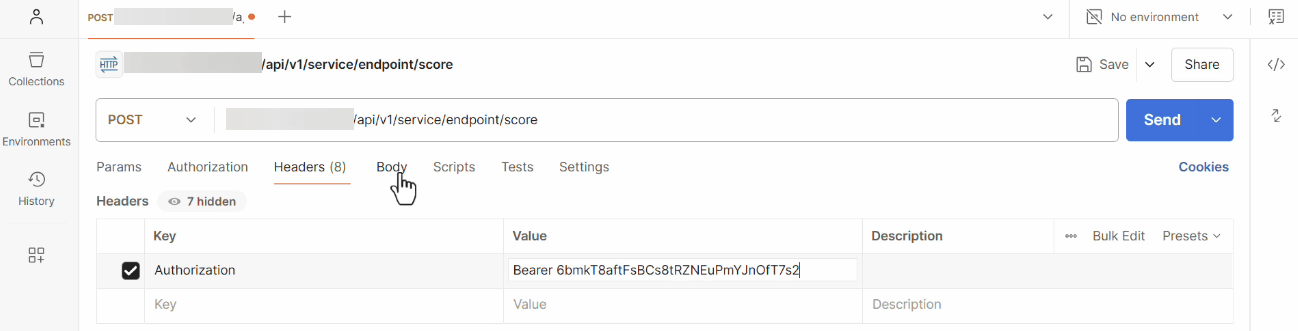
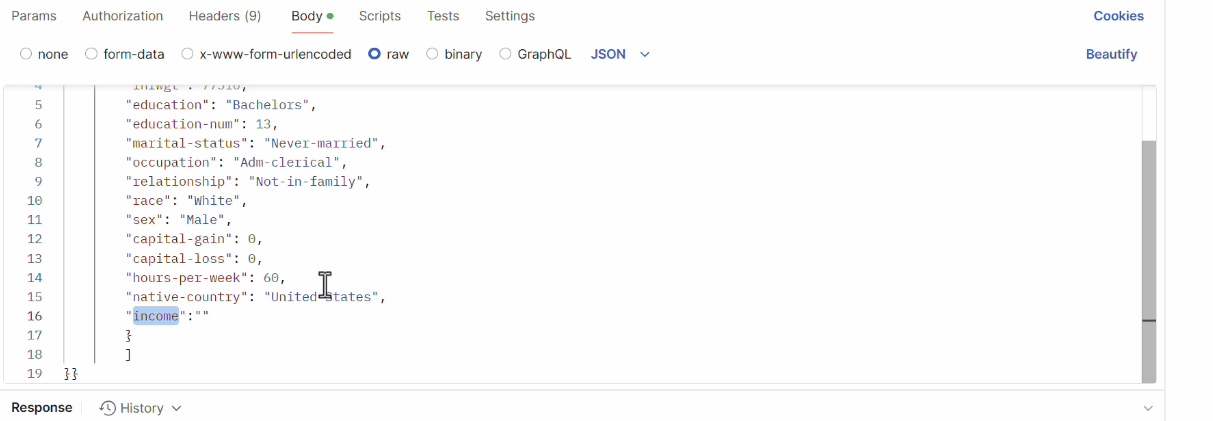
We can click the Send button to send our call. If everything has been configured correctly, we will receive an HTTP 200 OK response, which means that the service has successfully processed the request.
The response will contain the data processed by the service:
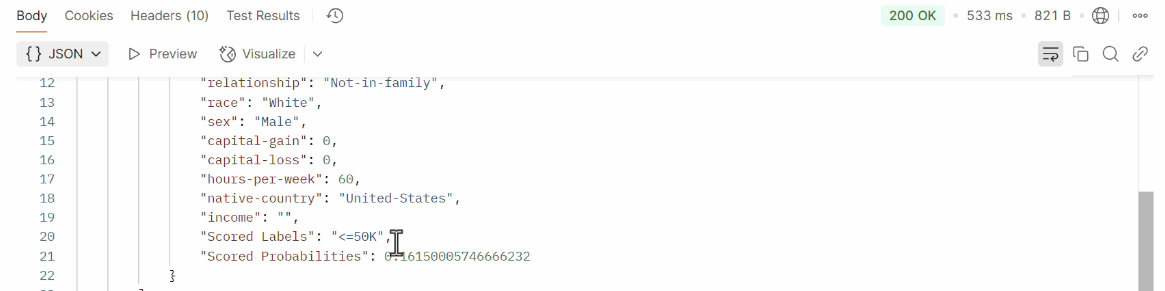
In case there is an error, such as an invalid authentication token or an error in the request format, we will receive an HTTP error code, such as a 400 Bad Request or a 401 Unauthorized.
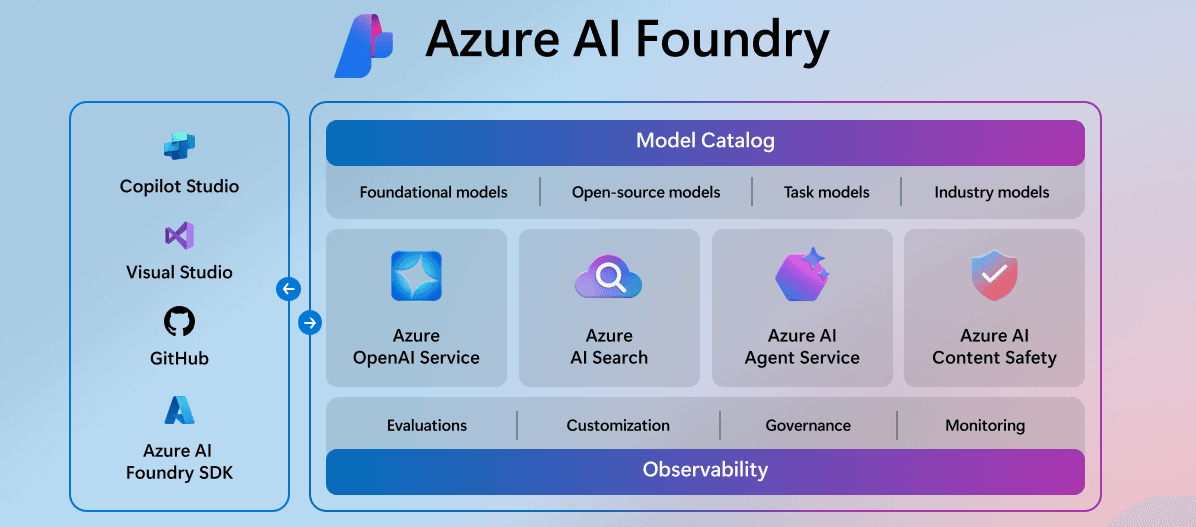
Azure AI Foundry
Azure AI Foundry is a comprehensive platform that bundles and integrates with all services for the advanced development of artificial intelligence-based applications.
The platform facilitates collaboration between development, data science, and business teams through the ability to manage projects, monitor model performance, and debug from a Hub.
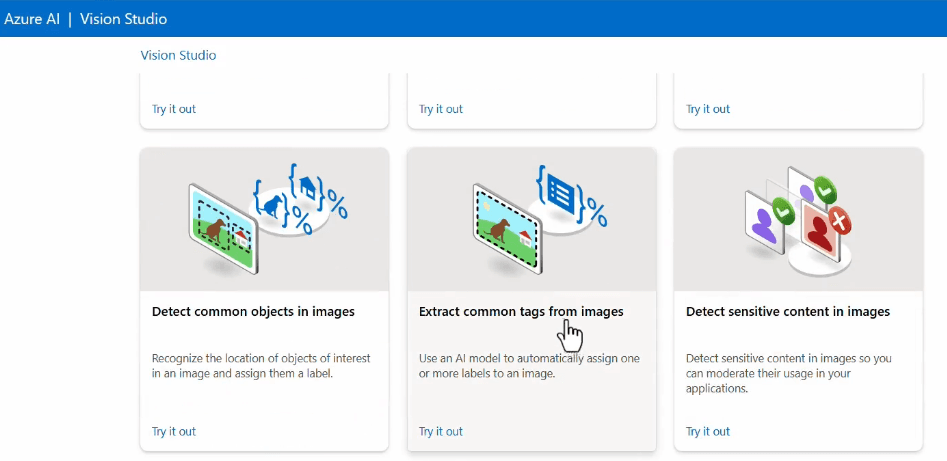
Example of a computer vision service
A practical example of the use of Azure's Computer Vision services is the Azure Computer Vision API, which analyzes images.
You can use this service in several ways: through the GUI offered by Azure AI Vision Studio or through the new Azure AI Foundry.

Each Azure service has detailed documentation.
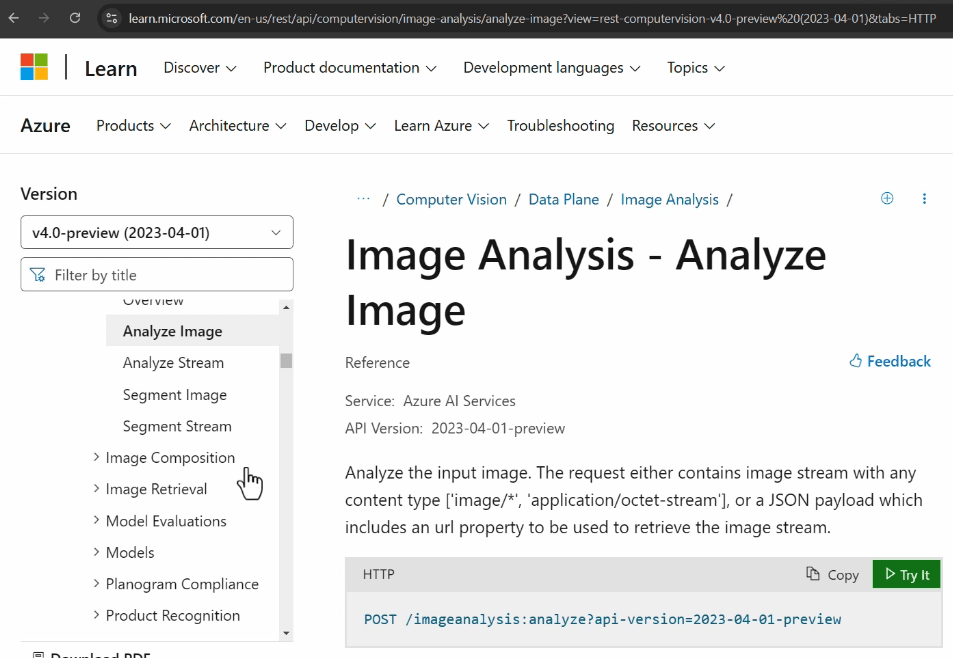
In the API reference of the service, the information needed to compose requests is available, including:
- Endpoint URL
- HTTP method
- Header & Body
- Input & format
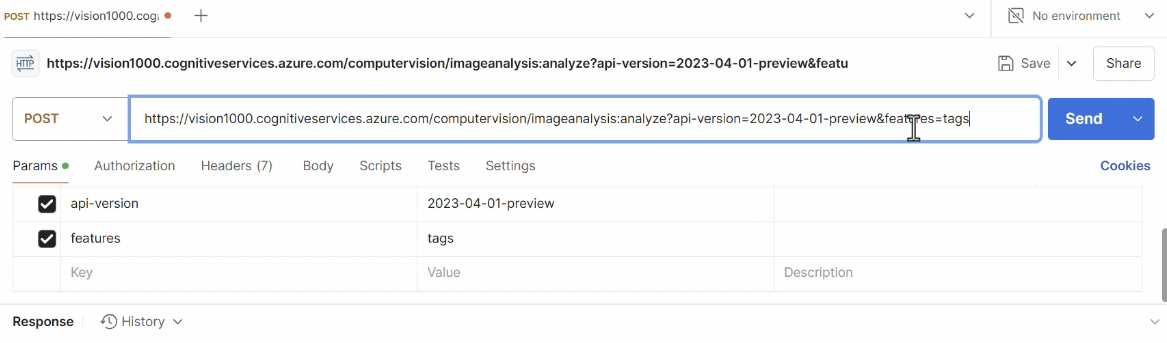
We then test the operation of this API using the Postman tool again:

References:
- https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/products/ai-services
- https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/ai-services/responsible-use-of-ai-overview
- https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/products/ai-foundry
- https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/ai-services/reference/rest-api-resources
Introduzione
L’intelligenza artificiale è diventata ormai parte nella nostra quotidianità, modificando in modo significativo il nostro approccio al lavoro, alla comunicazione e ai processi decisionali. Il potenziale completo dell’IA emerge quando viene abbinata alla scalabilità e alla potenza del cloud computing, permettendo di addestrare e distribuire modelli complessi su ampia scala con agilità e flessibilità.
In questo scenario, Microsoft Azure si posiziona come un leader nel democratizzare l’accesso a queste tecnologie, offrendo una piattaforma versatile per l'integrazione dell'IA nei processi aziendali.

Concetti fondamentali
Per comprendere il potenziale dell’intelligenza artificiale, è essenziale partire dalle sue fondamenta. L'IA si basa su modelli matematici e algoritmi che vengono addestrati. Essa è una disciplina che si concentra sullo sviluppo di sistemi in grado di simulare il comportamento umano.
Tra le sue componenti principali vi è il Machine Learning (ML), metodo centrale attraverso cui i sistemi apprendono dai dati, migliorando la loro comprensione senza necessità di programmazione esplicita. In altre parole, consente ai modelli di identificare connessioni e tendenze chiamate pattern all’interno di grandi insiemi di dati, per svolgere compiti.

Un aspetto fondamentale del Machine Learning è il training dei modelli, un processo che consiste nell’alimentare il sistema con dati etichettati (o meno) per "insegnargli" a fare previsioni. Ad esempio, un modello può essere addestrato a riconoscere email spam o non spam analizzando migliaia di esempi pregressi.
Le applicazioni del ML possono essere suddivise in tre categorie principali: classificazione, come distinguere immagini di gatti da quelle di cani, identificare oggetti etc..; regressione, come prevedere il prezzo di una casa basandosi su caratteristiche come posizione e metratura; e clustering, come raggruppare utenti con comportamenti simili in un sito web per personalizzare la loro esperienza.
Una significativa evoluzione nel campo è rappresentata dal Deep Learning, che utilizza reti neurali ispirate al funzionamento del cervello umano. Questo approccio è alla base di tecnologie avanzate come il riconoscimento vocale e i Large Language Models (LLM) come quelli utilizzati in sistemi di IA generativa.
Tra i Large Language Models (LLM) più noti e utilizzati al momento ci sono:
- GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer) di OpenAI: utilizza miliardi di parametri per rispondere alle domande;
- LLaMA di Meta: modello open-source progettato per essere più leggero;
- Claude di Anthropic: la filosofia del modello è basata sull'uso responsabile.
Il cuore del successo di questi modelli risiede nel processo di training e validazione. Dopo il training, il modello viene testato su un data set separato per valutare la capacità di generare output, passaggio fondamentale per evitare il problema dell’overfitting, in cui un modello risponde bene solo ai dati di training ma fallisce su dati nuovi.
Principali casi d'uso
Tra i principali casi d’uso troviamo:
- Predictions and forecasting: la capacità di analizzare dati storici per prevedere eventi futuri, come il comportamento dei clienti o la domanda di mercato;
- Anomaly detection: individuare deviazioni dai pattern di utilizzo normali, essenziale per la sicurezza, il monitoraggio delle frodi e il mantenimento di sistemi complessi;
- Natural language processing (NLP): l’abilità di prendere del testo, comprenderlo e rispondere in modo adeguato, come accade nei sistemi di traduzione o nelle analisi di sentiment;
- Computer vision: la capacità di processare immagini e restituire informazioni, ad esempio nel riconoscimento di oggetti, volti o situazioni nelle immagini e nei video;
- Conversational AI: consentire alle macchine di comunicare con gli esseri umani tramite conversazioni fluide e naturali, come nei chatbot o negli assistenti virtuali;
Questi casi d’uso rappresentano solo una parte delle incredibili possibilità offerte.
Machine Learning Vs Deep Learning
Machine Learning, Deep Learning e Natural Language Processing sono tre aree fondamentali dell'intelligenza artificiale, ma ciascuna di esse si concentra su aspetti diversi della "comprensione" e "interazione" con i dati.
- Machine Learning (ML) è una branca dell'IA che si concentra sullo sviluppo di algoritmi in grado di apprendere dai dati.
- Deep Learning (DL) è una sottocategoria di machine learning che si concentra sull'uso di reti neurali profonde, cioè modelli di machine learning con molteplici strati (layer). Questi modelli sono progettati per simulare il funzionamento del cervello umano e sono particolarmente potenti quando si tratta di lavorare con grandi volumi di dati non strutturati, come immagini, audio o testo. Il deep learning è alla base di tecnologie come il riconoscimento vocale, la visione artificiale (come il riconoscimento facciale) e la traduzione automatica.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP) si concentra sull'interazione tra computer e linguaggio umano. Può fare uso di tecniche sia di machine learning che di deep learning per migliorare la comprensione del linguaggio.

Ci sono poi altre aree importanti come la Computer Vision che consente ai computer di "vedere" e comprendere il contenuto di immagini e video. Altre sono ancora in fase di sviluppo come la Quantum Computing, la quale sfrutta i principi della meccanica quantistica per elaborare informazioni che non sono possibili con i tradizionali supercomputer.
Modelli
Per creare un modello di machine learning, il primo elemento fondamentale è un algoritmo, ovvero un insieme di istruzioni che il modello utilizza per apprendere dai dati. In termini semplicistici, possiamo immaginare un modello come una funzione matematica, rappresentata dalla formula y=f(x), dove x rappresenta gli input (dati) e y l’output (risultato previsto).
Un concetto centrale nella costruzione di un modello è il ruolo delle funzionalità (feature) e delle etichette (label) all’interno del dataset di training.

Le funzionalità sono gli attributi o variabili indipendenti che descrivono i dati, mentre le etichette sono il risultato o la variabile dipendente che vogliamo prevedere. Ad esempio, in un dataset che analizza il comportamento degli utenti, una funzionalità potrebbe essere "tempo trascorso sul sito", mentre l’etichetta potrebbe essere "acquisto effettuato: sì/no".
Prima di poter utilizzare i dati per l'apprendimento, è essenziale sottoporli a un processo di preparazione ed elaborazione (ETL: Extract, Transform, Load). Durante questa fase, ispezioniamo i dati per assicurarci che siano puliti e pronti per l'uso, rimuovendo valori mancanti, gestendo outlier e trasformando le informazioni in un formato adatto. Inoltre, possiamo applicare tecniche di feature engineering per creare nuove funzionalità basate su quelle esistenti, migliorando così le prestazioni del modello.
Gli algoritmi, una volta applicati ai dati, possono essere distinti in diverse categorie di apprendimento:
- Supervisionato: il modello apprende da un dataset etichettato, dove ogni input è associato a un output noto (ad esempio, classificazione o regressione).
- Non supervisionato: il modello lavora su dati non etichettati e cerca di trovare pattern nascosti o gruppi (ad esempio, clustering);
- Semi-supervisionato: una combinazione dei due approcci, in cui solo una parte dei dati è etichettata;
- Reinforcement learning: il modello apprende attraverso un sistema di ricompensa e penalità, adattandosi continuamente in base al feedback (ad esempio, nei giochi o nei sistemi di guida autonoma).
Cosa sono i Transformer?
I Transformer sono un'architettura di rete neurale progettata per gestire dati sequenziali (come testo, immagini o audio), introducendo un meccanismo chiamato self-attention, che permette al modello di analizzare l'intera sequenza simultaneamente e assegnare un peso a ciascun elemento rispetto agli altri. Sono particolarmente bravi a catturare le relazioni tra le parole, anche se sono lontane tra loro in una frase.

Esempio: Immagina che tu stia usando un Transformer per completare la frase: "Il cielo è molto..."
- Input: ["Il", "cielo", "è", "molto"]
- Self-Attention: Ogni parola cerca relazioni con le altre (es. "molto" dà attenzione a "cielo")
- Output: Il modello genera una parola probabile, come "azzurro"
Questo processo viene ripetuto parola per parola, fino a completare l'intera frase.
Cosa sono i Token?
I token sono unità di base in cui un modello di linguaggio, come un Transformer, scompone il testo per comprenderlo (capire) e manipolarlo. In un contesto linguistico, può rappresentare: parole, parti di parole, caratteri speciali o simboli, frasi o concetti.
Quando un modello di linguaggio riceve del testo come input, prima di tutto lo scompone in token. Questo processo si chiama tokenizzazione. Ogni token è quindi associato a una rappresentazione numerica, che il modello usa per comprendere la sequenza di testo. Questi vettori numerici vengono quindi elaborati dal modello (tramite il meccanismo di attenzione nel caso del Transformer) per generare output, come risposte, traduzioni, o predizioni.
I modelli hanno una lunghezza massima di token che possono elaborare, ad esempio GPT-3 può elaborare fino a 4096 token in un singolo input, mentre GPT-3.5 Turbo 16k arriva a 16000.
Più lunga è la sequenza, più token vengono utilizzati, e questo può influenzare il costo computazionale e la qualità delle risposte.
Esempio: Immagina di avere la frase: "Ciao, come stai?"
Un semplice processo di tokenizzazione potrebbe scomporla in:
- "Ciao"
- ","
- "come"
- "stai"
- "?"
Nat.dev
Nat.dev è una piattaforma progettata per facilitare l'interazione con i modelli di linguaggio avanzati, permettendo agli sviluppatori di esplorare, testare e utilizzare modelli linguistici moderni. Offre un playground, ossia un ambiente interattivo che consente la personalizzazione di parametri e impostazioni per osservare come il comportamento di un modello varia in base alle diverse variabili.

Variabili e parametri
Quando interagiamo con un modello di linguaggio avanzato ci sono diverse variabili o parametri che possiamo modificare per influenzare il comportamento e i risultati generati in modo da ottenere risposte più creative, coerenti, o adatte a specifiche esigenze.
La temperatura è uno dei parametri principali per controllare la creatività e la casualità delle risposte. Una temperatura più bassa (es. 0.2) rende il modello più deterministico e preciso, mentre una temperatura più alta (es. 1.0 o superiore) rende le risposte più creative, imprevedibili e diverse.
Top-p (conosciuto anche come "nucleus sampling") è un altro parametro di controllo della creatività, che stabilisce la probabilità cumulativa da cui il modello attinge le risposte. Un top-p basso (es. 0.2) per risposte più prevedibili. Un top-p alto (es. 0.9) per aumentare la varietà nelle risposte.
La frequency penalty per la ripetizione di parole o frasi. Aumentando questo parametro, si riduce la probabilità che il modello ripeta le stesse parole o concetti in modo ridondante. Un valore più alto aumenta questa penalizzazione.
La presence penalty disincentiva l'uso di parole che sono già apparse nel contesto della conversazione. Maggiore è il valore, minore sarà la probabilità che il modello ripeta argomenti o parole già usate.
Le Stop sequences indicano al modello quando fermarsi nella generazione della risposta. Puoi definire una o più sequenze di testo che, se generate dal modello, lo faranno fermare immediatamente. Questo è utile per evitare risposte troppo lunghe o non desiderate.
Logit bias è un sistema che permette di modificare la probabilità che certe parole o frasi vengano scelte dal modello. Consente di forzare il modello a favorire (o evitare) specifiche parole nei suoi output, alterando il logit (la misura della probabilità) di certe scelte.
Prompt
Il prompt è senza dubbio uno degli elementi più cruciali quando si interagisce con un modello. Si tratta del testo (la domanda) che forniamo come input, la sua importanza non può essere sottovalutata, poiché guida completamente la risposta che otterremo (funge da direttiva). Se fornisci un prompt ambiguo o generico, la risposta sarà probabilmente altrettanto generica. Ma se il prompt è preciso e chiaro, la risposta sarà dettagliata, pertinente e utile. Puoi usare il prompt per influenzare il tono e lo stile della risposta. Un prompt mal formulato può portare a risultati errati o irrilevanti.

Un esempio di come un prompt ben formulato incide sul risultato finale si vede nei modelli text-to-image come Midjourney. Qui, la qualità del prompt determina direttamente l'output visivo. A differenza dei modelli linguistici, dove valutiamo coerenza e tono, in text-to-image il legame tra prompt e immagine è immediato e visibile.
Servizi Azure
Microsoft Azure offre una vasta gamma di servizi cloud che permettono alle aziende di implementare soluzioni intelligenti sfruttando l'intelligenza artificiale e il machine learning. Questi servizi si collocano in un ecosistema che include tutto, dalla gestione dei dati al training dei modelli fino al deploy di applicazioni.
Tra questi emergono due soluzioni principali:
- Azure Machine Learning
- Azure Cognitive Services
Le differenze tra le due soluzioni si concentrano principalmente sull'approccio adottato per l'implementazione dell'intelligenza artificiale, sulla possibilità di personalizzazione e sul livello di controllo consentito sugli algoritmi e sui modelli.
Azure Cognitive Services è un set di API e servizi IA pre-costruiti da Microsoft (non è possibile personalizzarli per casi d'uso specifici se non in modo limitato). Questi servizi consentono agli sviluppatori di aggiungere intelligenza artificiale alle applicazioni senza dover costruire o addestrare modelli. Include riconoscimento del linguaggio naturale, visione artificiale, riconoscimento vocale e analisi del sentiment del testo. È utile per progetti che richiedono funzionalità standard come i chat-bot.
Azure Machine Learning è una piattaforma gestita per sviluppare, addestrare e distribuire modelli di machine learning complessi. Ideale per data scientist e sviluppatori che vogliono creare modelli personalizzati con algoritmi avanzati. E' possibile scegliere gli algoritmi da utilizzare, definire il flusso di lavoro, e addestrare i modelli su dataset specifici. Fornisce il controllo completo su algoritmi, flusso di lavoro e training dei modelli.

Creazione e uso del servizio AML
La creazione del servizio nel portale Azure è un processo che prevede diverse fasi:
- Il primo passo è la creazione di un workspace, un area di lavoro che funge da contenitore per tutti gli oggetti, i dati, i modelli etc.. rappresenta il punto centrale dove verranno organizzate tutte le attività;
- La creazione di un workspace richiede una serie di risorse aggiuntive per gestire in modo efficiente i dati, la sicurezza e il monitoraggio delle operazioni: Azure Key Vault, Azure Storage Account, Azure Container Registry, Application Insights. Queste risorse vengono configurate automaticamente o manualmente durante la creazione dell'ambiente.
Una volta configurato il workspace il prossimo passo è aprire Azure Machine Learning Studio, una piattaforma grafica che consente di creare e gestire in modo visivo e interattivo.
Lo studio consente di caricare facilmente i dati o usare campioni esistenti, che si possono dividere in set come training (70%) e test/validation (30%).
Il Designer è una delle funzionalità più potenti in quanto, con un approccio no-code e drag & drop, permette di costruire il flusso del modello governandone l'intero ciclo di vita.
Con il flusso costruito si può procedere all'addestramento del modello, e una volta terminato fare il test e la validazione. Il sistema permette anche di monitorare le metriche in tempo reale, come la precisione e il recall per modelli di classificazione e altri parametri di performance.
Una volta che il modello è pronto il passo successivo è il deployment, utlizzando le varie opzioni di Azure Compute:
- Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS): Se desideri un ambiente scalabile e altamente disponibile;
- Azure Container Instances (ACI): Un'alternativa più semplice e leggera, se il modello non ha bisogno di scalabilità o di una gestione complessa;
- Edge Computing: In alcuni casi, potresti voler implementare il tuo modello direttamente su dispositivi edge (ad esempio, IoT)
Endpoint del servizio
Quando si parla di AI Services in Azure, uno degli aspetti fondamentali riguarda l'interazione con i servizi attraverso gli endpoint. Un endpoint rappresenta un'URL specifico che consente di invocare un servizio mediante una chiamata API. A tali URL vengono inviate richieste per ottenere o inviare dati, come ad esempio immagini, testo o parametri di input.

Una volta recuperato è possibile testarlo tramite una richiesta REST. Gli strumenti più utilizzati per testare e interagire con le API RESTful sono Postman o cURL.
Interagire tramite Postman
Nel caso specifico di una chiamata di tipo POST, stiamo passando delle informazioni al servizio per ottenere una risposta elaborata. Questa è la modalità più comune quando lavoriamo con dati che devono essere processati, come ad esempio il testo o le immagini.
Per inviare una richiesta di questo tipo, dobbiamo configurare correttamente due parti:
- Header: con le informazioni di autenticazione necessarie, utilizziamo un bearer token che rappresenta il nostro permesso di accesso al servizio generato durante la creazione del servizio;
- Body: dobbiamo specificare i dati che vogliamo inviare al servizio, per questo tipo di servizio dobbiamo utilizzare il formato JSON, il corpo dovrà essere una stringa che contiene le informazioni necessarie per elaborare la richiesta.


Possiamo fare clic sul tasto Send per inviare la nostra chiamata. Se tutto è stato configurato correttamente, riceveremo una risposta HTTP 200 OK, che significa che il servizio ha elaborato la richiesta con successo.
La risposta conterrà i dati elaborati dal servizio:

Nel caso in cui ci sia un errore, come un token di autenticazione non valido o un errore nel formato della richiesta, riceveremo un codice di errore HTTP, ad esempio un 400 Bad Request o un 401 Unauthorized.
Azure AI Foundry
Azure AI Foundry è una piattaforma completa che raggruppa e si integra con tutti i servizi per lo sviluppo avanzato di applicazioni basate sull'intelligenza artificiale.
La piattaforma facilita la collaborazione tra team di sviluppo, data science e business, grazie alla possibilità di gestire progetti, monitorare performance dei modelli e fare debugging da un Hub.

Esempio di servizio computer vision
Un esempio pratico dell'uso dei servizi di Computer Vision di Azure è l'Azure Computer Vision API, che analizza le immagini.
È possibile utilizzare questo servizio in diversi modi: tramite l'interfaccia grafica offerta da Azure AI Vision Studio oppure tramite il nuovo Azure AI Foundry.


Ogni servizio di Azure dispone di una documentazione dettagliata.

Nell'API reference del servizio sono disponibili le informazioni necessarie per comporre le richieste, tra cui:
- Endpoint URL
- Metodi HTTP
- Header e Body
- Formati e input
Testiamo quindi il funzionamento questa API utilizzando nuovamente lo strumento Postman:




Riferimenti
- https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/products/ai-services
- https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/ai-services/responsible-use-of-ai-overview
- https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/products/ai-foundry
- https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/ai-services/reference/rest-api-resources
--